Product review generation using conditional generative language model
CSCI 566 2019 Fall Project (NLP TextGen)
Taejin Park, Yongwan Lim, Yichen Zhou, Kaixi Wang
[CODE] [SLIDES]
Motivation
The rise of deep neural-network based approaches has significantly improved natural dialog with machines in the past few years. While conditional generative models have been successfully deployed in image/video applications, there is still much that can be done with generative language models such as VAE [1] and GPT2 [2-3] in text and language applications.
Goal of this project
The goal of this project is to artificially generate semantically and syntactically correct product review comments given human inputted keyword prompts. Specifically, we are trying to address the question: Can we generate text while controlling the output? If we can control the output of generated text, we can apply this technique to many real life applications, including chat-bot, AI speaker, predictive text, and many others.
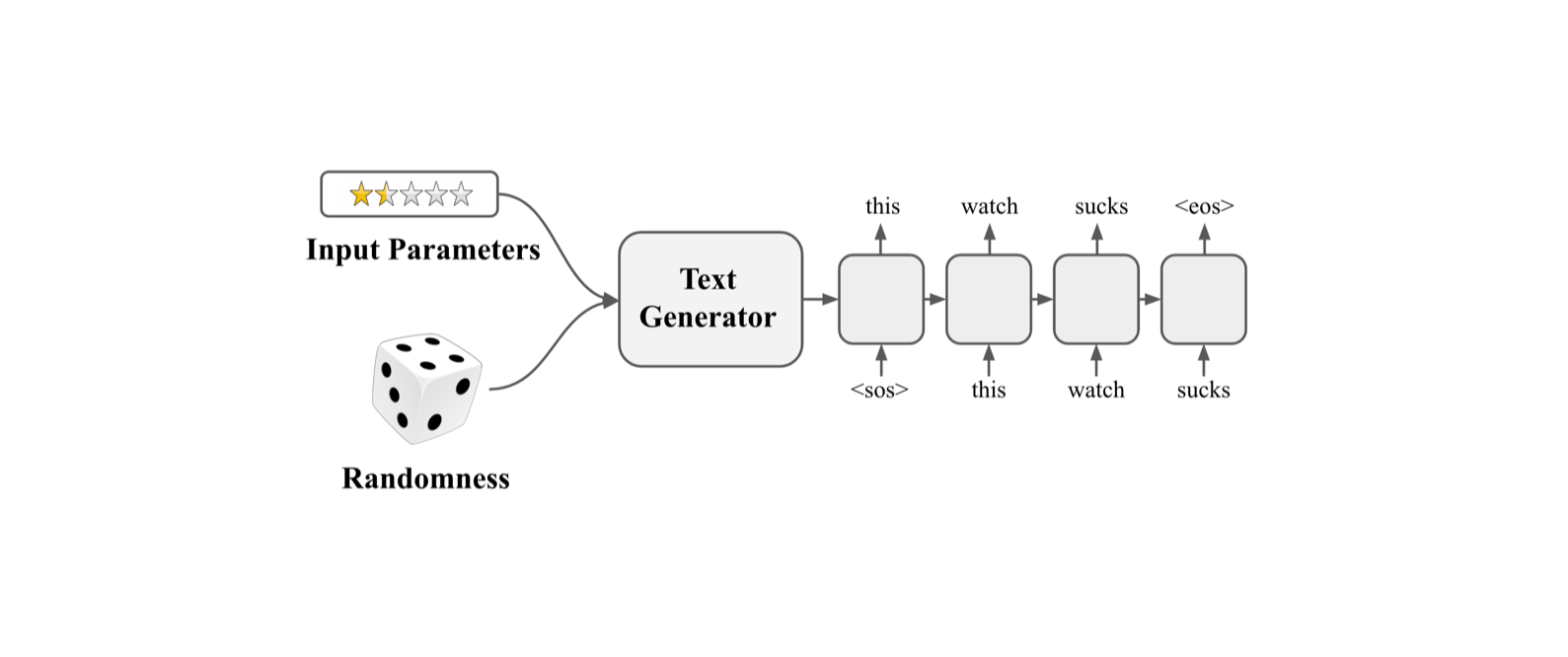
We expect this project to have the following features:
- Generative language model
- Keyword prompts input: sentiment (rating), subject (product name), aggressiveness (vocabulary)
- Grammatically correct sentence output that contains a distinct context
Problem Definition
To artificially generate semantically and syntactically correct review sentences given human inputted keyword prompts.
- Training input: review texts, rating 1 or 5
- Inference
- Input: review rating 1 or 5
- Output: review sentences containing and/or reflecting the given distinct context and sentiment
This would require us to being able to have randomness and controllability at the same time. The main challenges of this problem would be that:
- The generated output is often independent of the conditioning input (mode collapse).
- Quality of generated sentence (repetitive phrases, too general output)
Traditional Method
Conditional Variational Auto-Encoder (CVAE) [1]
Training
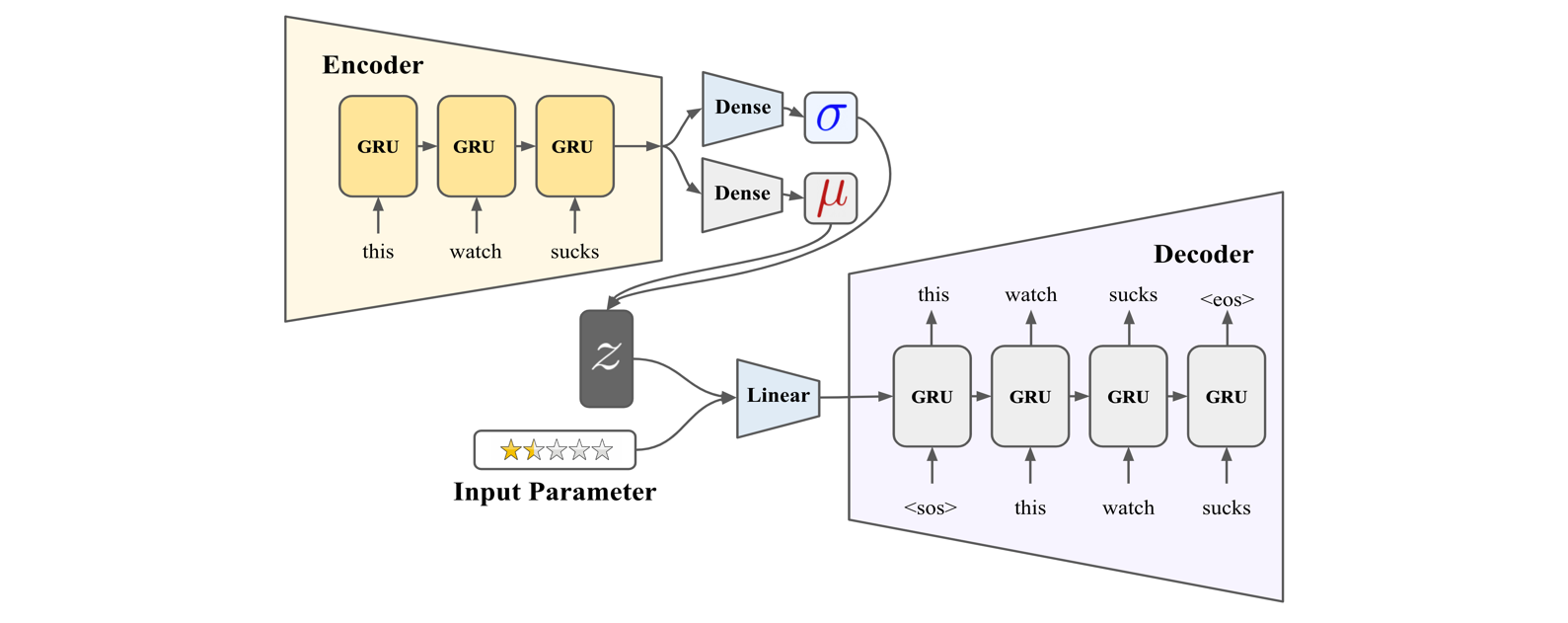
- Conditional VAE system that uses keyword/sentiment as conditional input.
- Both encoder and decoder take the keyword input during training.
Inference
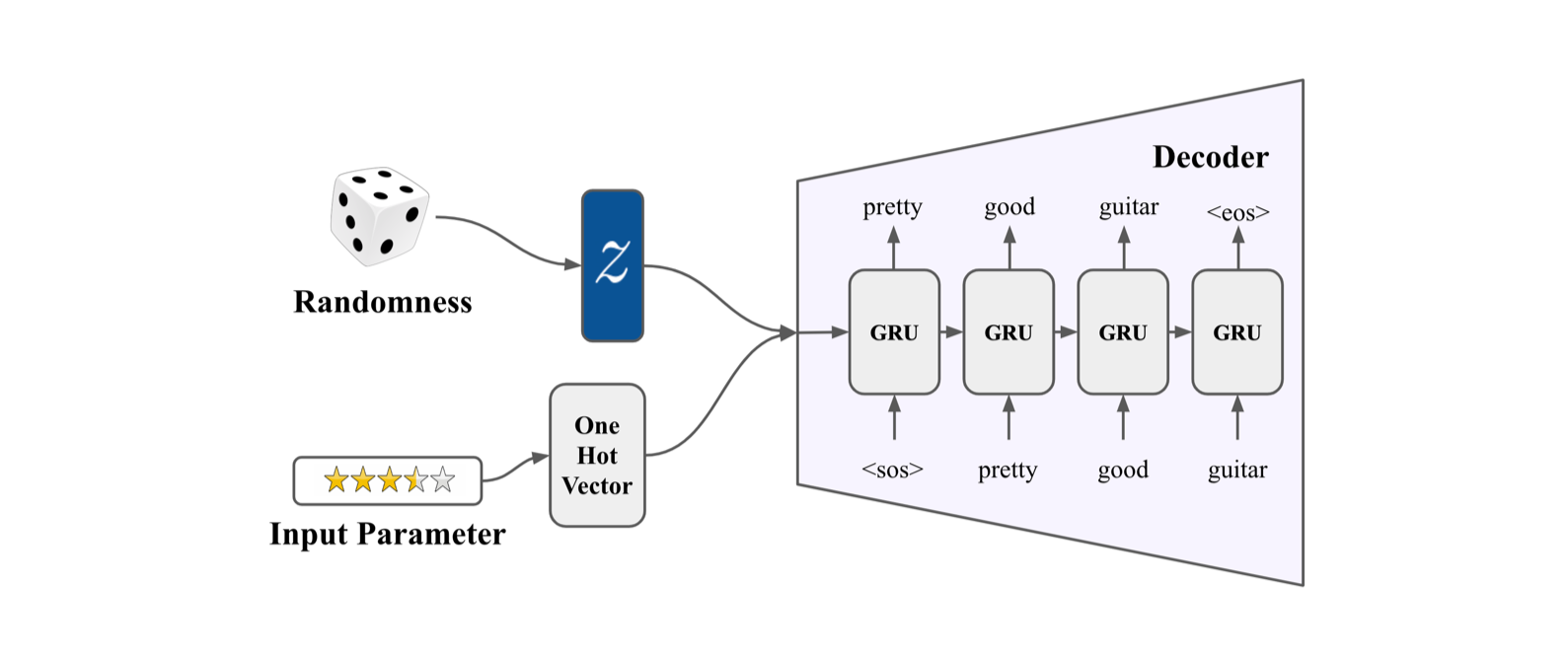
- Decoder outputs a few sentences of review about a product driven by keyword input.
- Random noise input can work as a seed for generated review.
- Limitation of conventional CVAE : the decoder ignores conditional input (mode collapse)
- Example:
- 1-star input, 100 noise samples ➝ 44 positive, 56 negative output
- 5-star input, 100 noise samples ➝ 61 positive, 39 negative output
- Even if we provide conditioning input to decoder, the sentiment is heavily dependent on random signal and conditioning input is not able to change the sentiment already ingrained in the random noise.
- Thus, we need more powerful and efficient way to enforce the sentiment to the training and inference systems.
- Example:
Proposed Method: Improved CVAE
Training (CVAE + Discriminator)
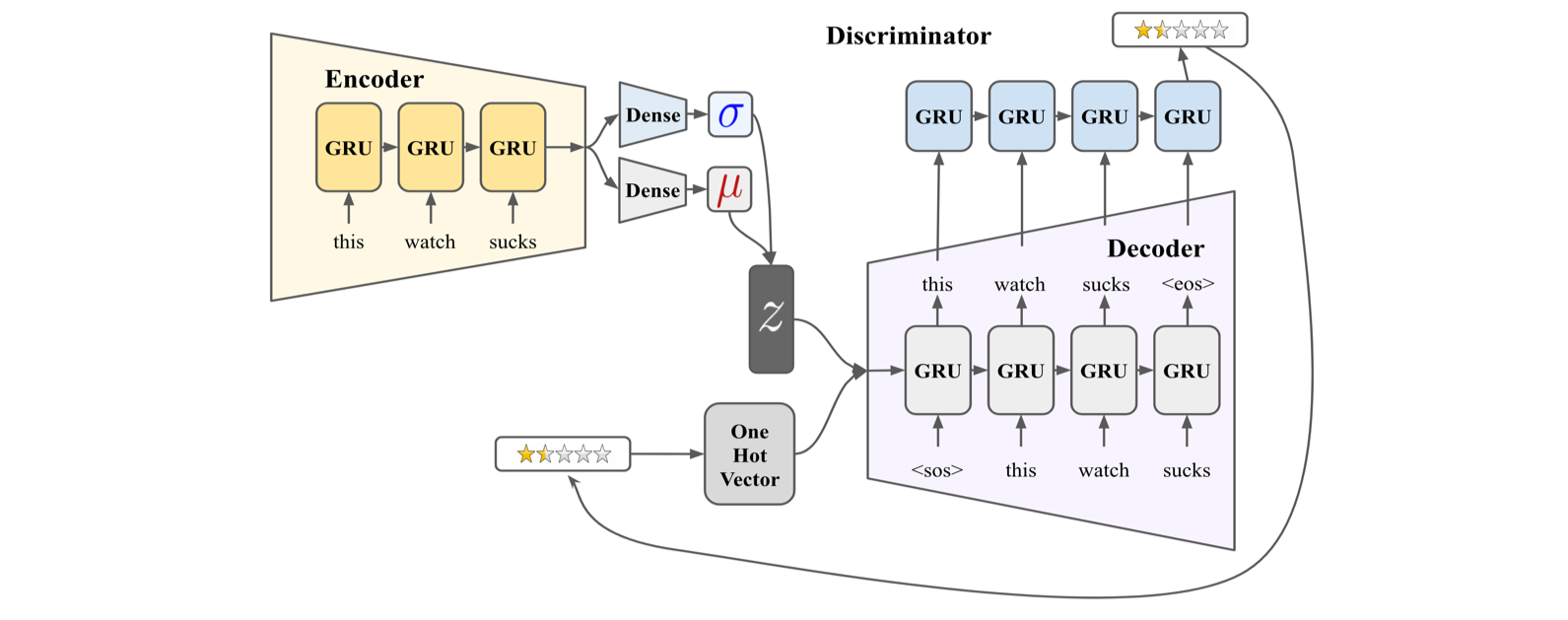
- Discriminator is a classifier that predicts sentiment of a word sequence generated by the decoder.
- Attaching discriminator enables the model to backpropagate the error from the sentiment (star rating) labels thus leads to more accurate sentiment.
Inference (Conditional Decoder + Discriminator + Filtering)
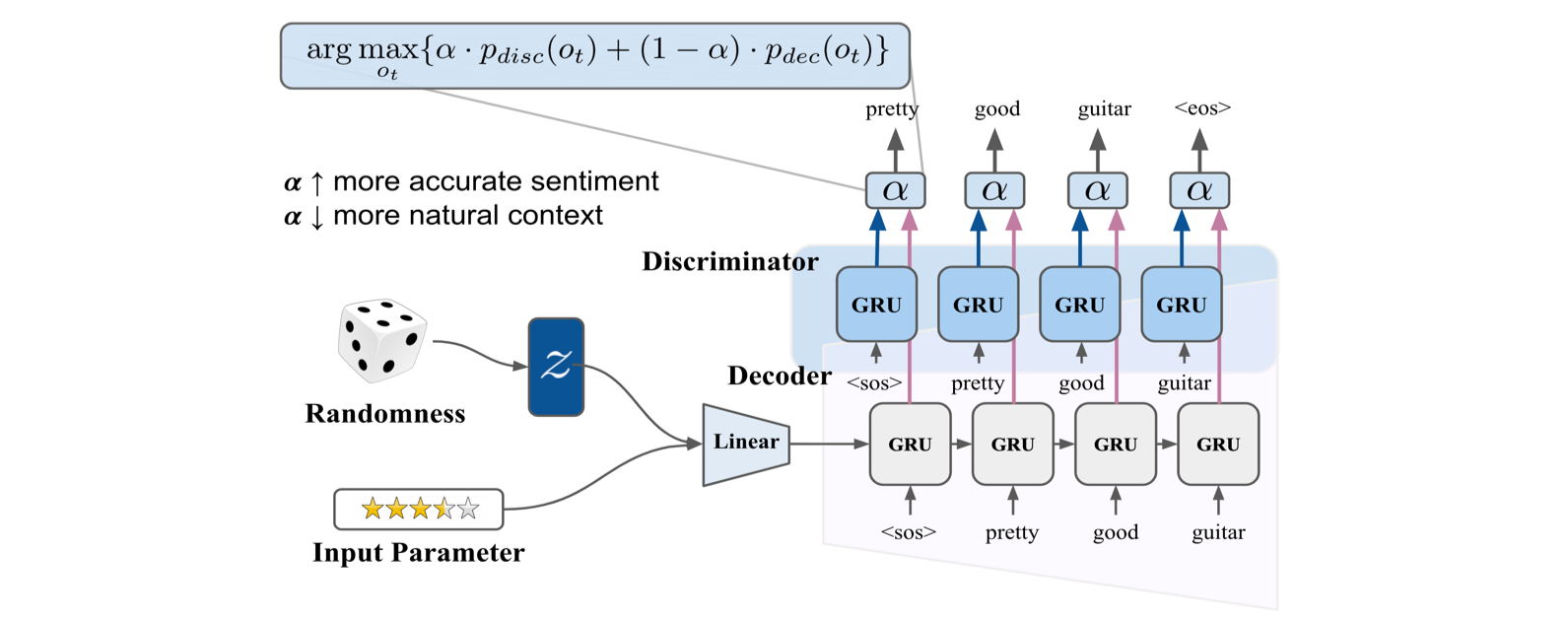
- Since conventional CVAE system ignores the conditioning input, we can force the conditioned word output by leveraging the discriminator.
- The alpha value balances between the softmax value from discriminator and the softmax value from the decoder.
- If the alpha value is close to 0, the model outputs very plausible and grammatically correct sentence but with inaccurate sentiment.
- If the alpha value is close to 1, the model generates a sentence that expresses more accurate sentiment but is often grammatically and semantically incorrect.
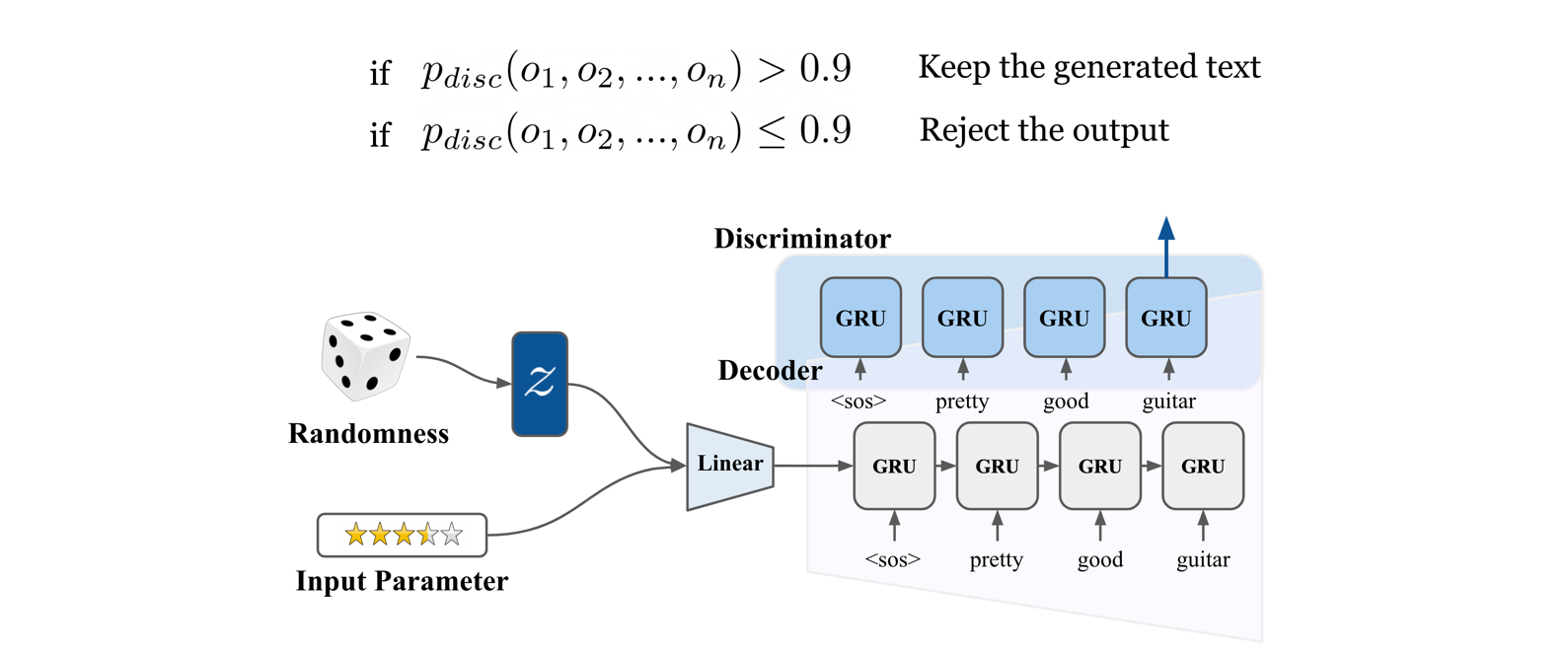
- If text output is not giving a certain amount of confidence in terms of softmax value of the discriminator, we drop the output text and regenerate it.
Neural Network Training
- Training Dataset: Amazon review dataset [4]
- Trained on a subset of 5 major categories (Electronics, mobile electronics, major appliances, and etc)
- Trained on total 0.6M reviews
- Vocabulary size of 60K words
- Limit sentence length between 20 and 60 words, including punctuations.
- Only use 1-star (negative) and 5-star (positive) ratings
- 66% negative / 33% positive data (*Since negative comments tend to have more variability, doubling the dataset of negative training data balances the variability of output text’s sentiment)
-
Example of training dataset:
Reviewer ID: R1KKOXHNI8MSXU
Product category: Apparel
Review text: “This is the second leggings I have ordered, I wear both of them often. They wash well and I receive many compliments on them!”
5-star rating of the product: 5
Helpful votes: 3
- Environment
- Pytorch 0.4.1, CUDA 10.0, Python 3.6
Experiments
We test the effectiveness of the proposed methods in terms of sentiment accuracy measure:
- Conditional decoder
- The conditional output accuracy is dependent on 𝜶.
- Check how output text varies over different 𝜶.
- Output filtering
- Rejects the output text with low discriminator output softmax probability
Sentiment accuracy is used as a performance metric, which is measured by BERT (Transformer) + LSTM sentiment classifier trained on IMDB dataset. For sanity check, we ensure that the classifier reaches accuracy of 92.31% for IMDB test set.
Evaluation
We evaluate the quality of artificially generated sentences along the following two dimensions:
- Evaluation by humans:
-
15 participants
- Task 1: Real vs Generated
- 48 comments; 24 real, 24 generated
- Machine generated texts are shuffled with human generated text.
- Evaluators were asked whether they think the review is generated by human or machine.
- Task 2: Sentiment Classification
- 48 comments; 24 1-star, 24 5-star
- Evaluators were asked whether they think the review is positive or negative.
-
- Evaluation by algorithm:
- BERT model-based Bi-LSTM sentiment classifier (the same system as in Experiments section)
-
Trained on IMDB data using BERT embeddings (IMDB test set accuracy: 92.31%)
- Task 2: Sentiment Classification
- 48 comments; 24 1-star, 24 5-star
Results
Control between sentiment and syntax
- Example of conditional decoder output of negative condition, star rating 1.

- If alpha is 0, there is no influence of discriminator, and it sometimes generates sentiment that does not correspond to the given sentiment (For a given star rating of 1 but alpha of 0, the sentence says “she loves it”)
- Higher alpha values show grammatical errors (e.g. These are a terrible product) or sentences do not make any sense (e.g. no distortion when it goes)
Improvement of sentiment accuracy by conditional decoder and output filtering
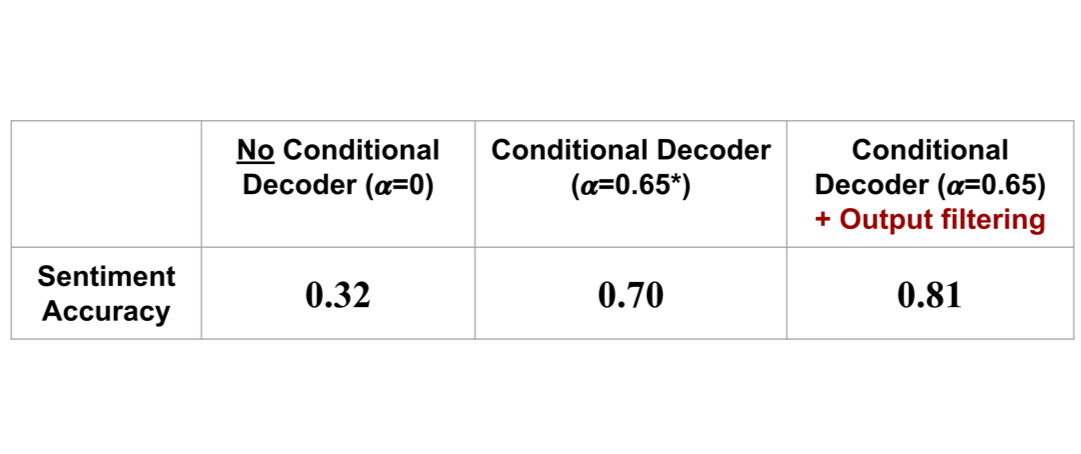
- Sentiment accuracy is evaluated with different 𝜶 and 𝜶=0.65 gives the best performance while showing a good balance between grammar and accurate sentiment.
- All the following evaluation is done with alpha value of 0.65.
Task 1: Real vs Generated
- Evaluation by Humans: Accuracy (F1 score): 70.83% (73.31%)
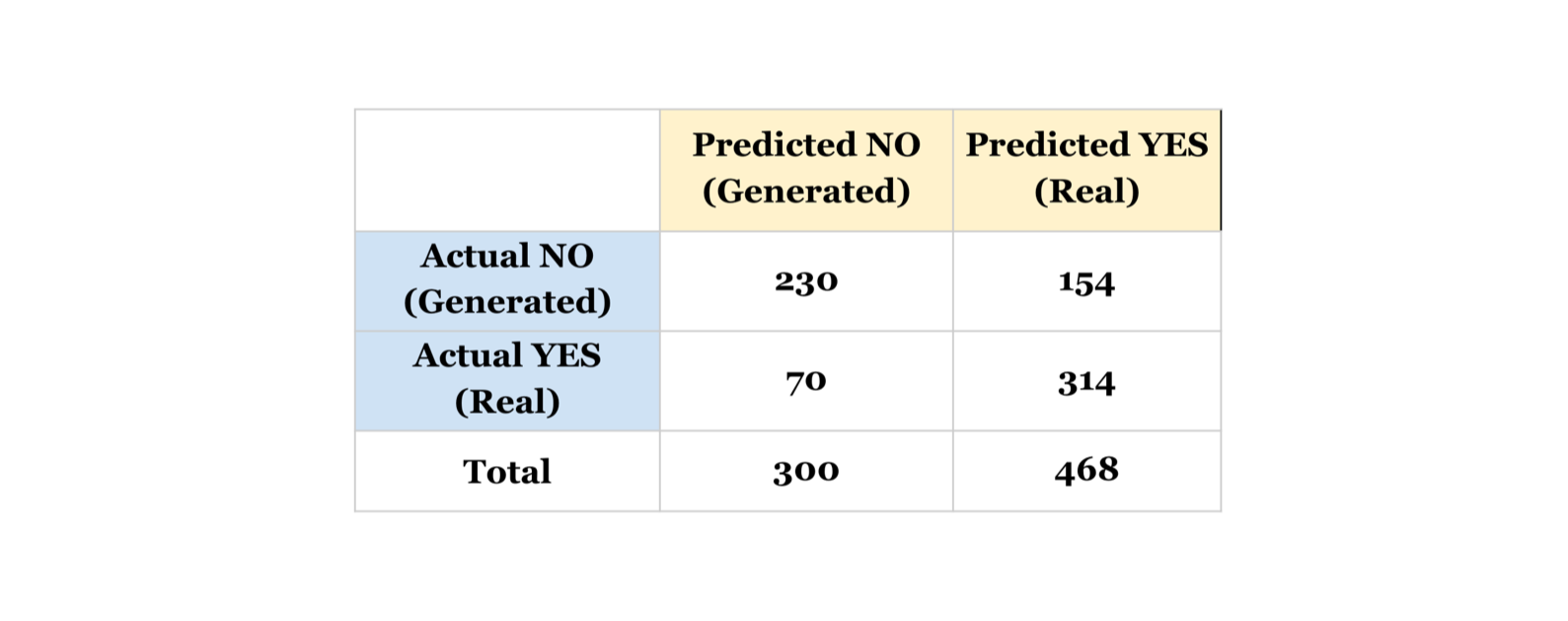
- 50% is chance probablity and this means that some texts are very plausible while some are not.
- Highlights of evaluation by humans
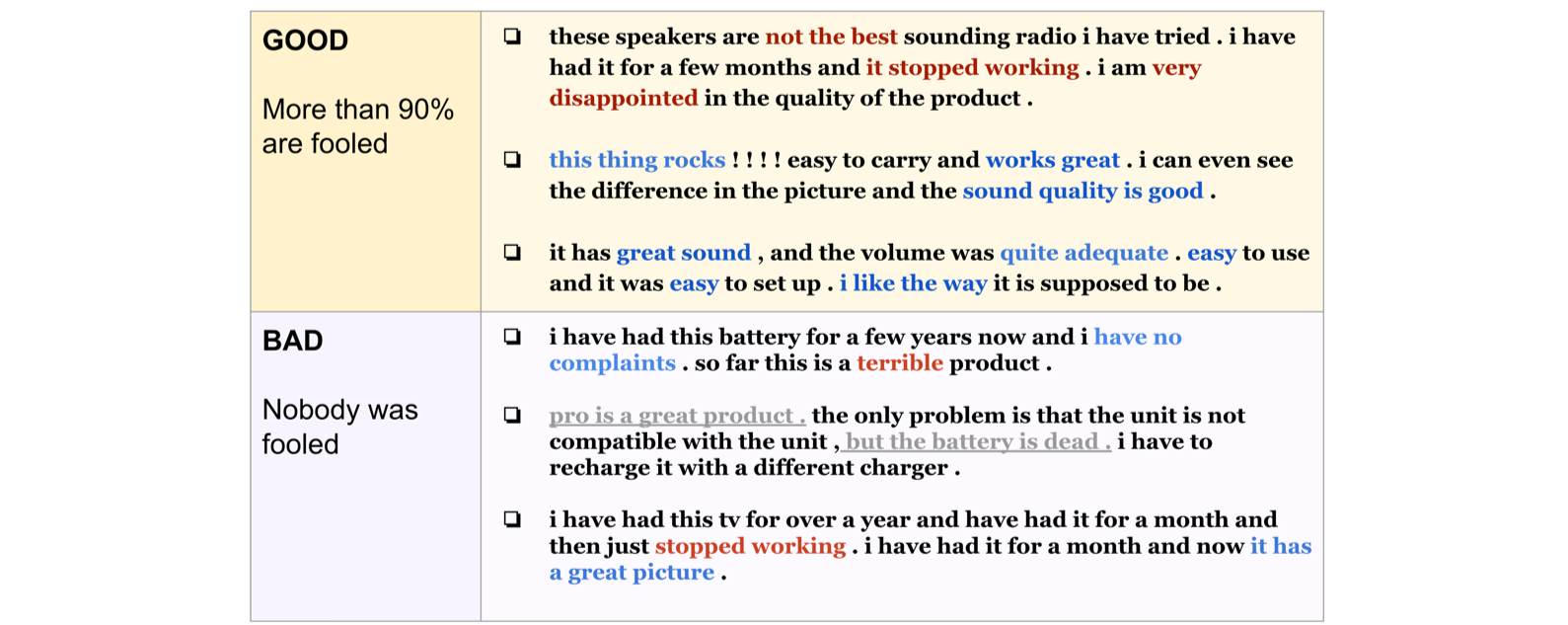
- We picked three sentences that all the human annotators said “Real” comments. These sentences show very consistent sentiment.
- We also picked three sentences that all the human annotators said “Generated”, which means failed output. These sentences show lots of conflicting sentiment and semantically incorrect phrases.
Task 2: Sentiment Accuracy
- Evaluation by humans: Accuracy (F1 score): 87.5% (88.00%)
- Ground truth: majority vote of annotated sentiment scores (0 generated or 1 real)
- Highlights of evaluation by humans

- We picked the sentences with coherent sentiment outcome from human annotators. These sentences have very consistent sentiment in each sentence.
- We also picked the sentences which have conflicting annotations. These sentences have inconsistent sentiment which means failed output.
- Evaluation by machine: Accuracy (F1 score): 77.08% (80.70%)
- This score is from the softmax value of positive/negative sentiment class in BERT + BiLSTM model trained on IMDB dataset.
- BERT + BiLSTM model tends to misclassify negative sentence as positive sentence since there are plenty of negative expressions that do not exist in IMDB dataset. (e.g. This plastic cover do not fit into my camera and very cheaply made.)
- Sentiment Score Comparison Machine vs Humans
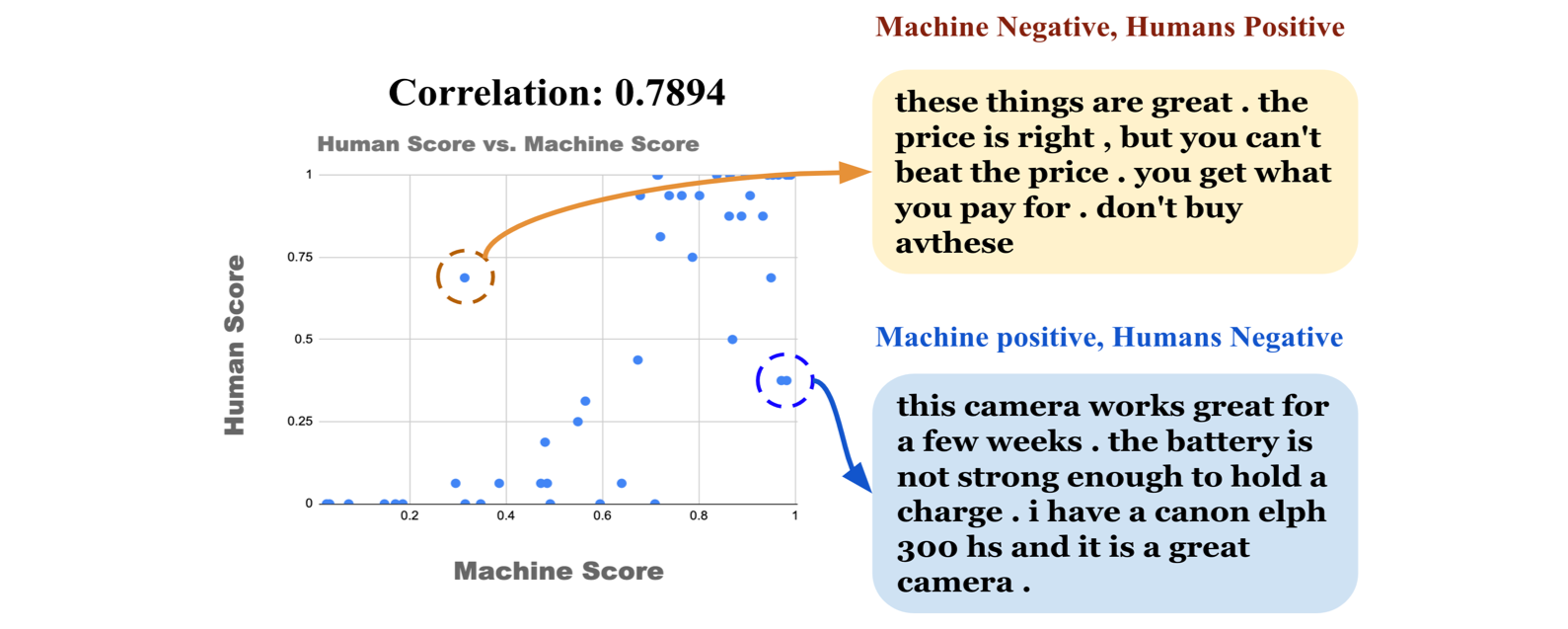
- This correlation reflects the credibility of algorithm (machine)-based evaluation.
- There are few highly conflicting outcomes: Human annotators are far better at capturing semantics from the text to judge the actual sentiment.
Additional Work: Pretrained model (GPT-2) based text generation
(CLICK) Product review generation using GPT2 model
- Click the above link to view the details.
- Besides our proposed improved CVAE model, we also approahced this problem with pretrained language model (GPT-2).
- For pretrained language model, we fined tuned the model with refined training dataset by filtering “helpfulness” in amazon review dataset.
- Here are some examples from fine-tuned GPT-2 based text generation system:
| Score | Headline | Review |
|---|---|---|
| 5 | I would buy those again | I absolutely love these, even though the price was such that I did not get them in time. The sound is amazing and I would recommend these. |
| 2 | This item never came | If you are looking at something for cheap, it would be very nice to receive an item that never came. This item did not come after 2 weeks. I emailed Amazon who did not even respond to my email. |
| 5 | Just what I was looking for | My husband is always wanting to get a Bluetooth headset and has now found the ideal one in my pocket. It holds his music perfectly and is comfortable. It also has great sound quality for listening to music. Great sound, great built-in mic, and the Bluetooth connection works wonderfully. My husband can use his laptop to play his MP3 player while he works. The speakers work just fine on it. It is a bit loud but I get it loud. The headphones are very long and this is a great fit for those who want an outside ear, as well as others who require some sort of earbud. All in all, a great product for such a reasonable price. |
Conclusion
- The challenge of ignored condition
- Input condition to CVAE can be ignored and lead to mode collapse.
- Conditional generative model should be carefully designed to avoid ignored condition problem.
- Conditional decoder and output filtering
- Conditional decoder leverages the discriminator’s ability to force the condition input.
- Output filtering also improves the quality of generated text.
Future Work
- Consistency of sentiment:
- Time varying conditional decoder’s 𝜶 value that controls the condition
- Self attention algorithm to focus on the certain part of the generated text.
- Generative method coupled with CVAE+Discriminator
- A way to modify the random input to prevent the condition ignoring problem
Reference
[1] K. Sohn, H. Lee, and X. Yan. Learning Structured Output Representation using Deep Conditional Generative Models. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. 2015.
[2] A. Radford, J. Wu, R. Child, D. Luan, D. Amodei and I. Sutskever. Language Models are Unsupervised Multitask Learners. 2019.
[3] GPT-2 Model release: https://www.openai.com/blog/better-language-models/
[4] Amazon review dataset: http://jmcauley.ucsd.edu/data/amazon/
Written by Yongwan Lim and Taejin Park on Dec. 5. 2019